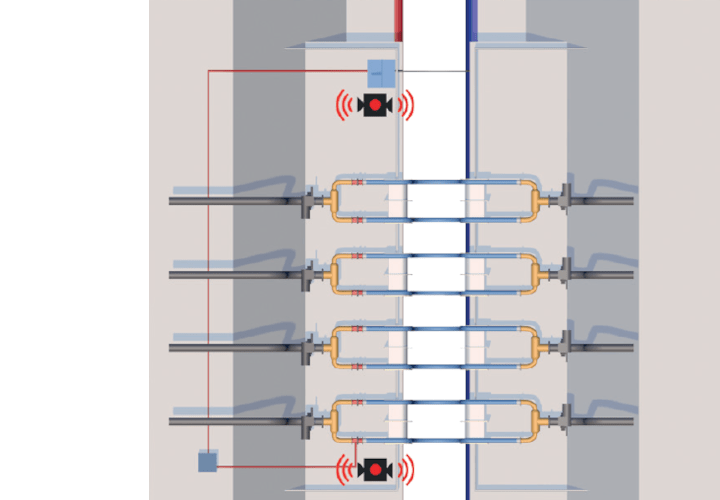
An example of KLAW LNG ESD Bulk Transfer operation
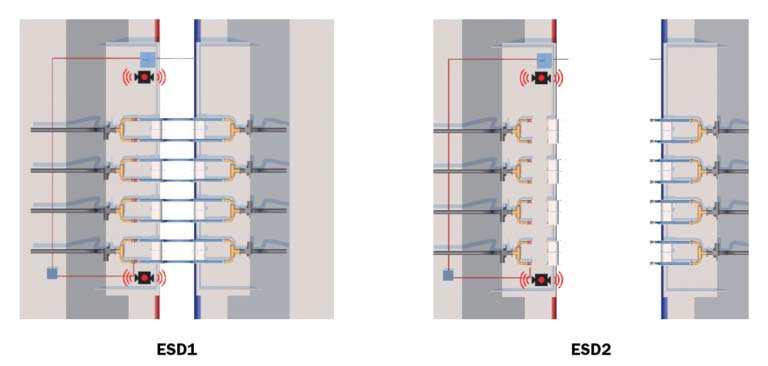
If the Feeder Vessel (LNG Carrier) and Receiving Vessel (FSRU) drift apart during a LNG Transfer operation, the ESD-1 will initiate at 5m drift and ESD-2 will initiate at 7m drift. A cause of vessel drift might be failure of the mooring system.
ESD1 and ESD2 protocols: Bulk LNG Transfer example
The ESD-1 will stop the transfer of LNG between the vessels by shutting the LNG transfer pumps on the FSRU and closing the ESD-1 manifold valves on both vessels.
The ESD-2 release function will ensure that the hoses are never fully extended before release is affected. The objective of ESD-2 is therefore the safe and controlled “dry break” of the transfer hoses.
The ESD system allows for manual control and therefore the execution of procedures on board the vessel.
If alternative diameter fenders or different mooring configurations are used then the drift tolerances will be adapted to suite the particular arrangement.
KLAW LNG has a range of ESD formations and specifications designed for different applications and circumstances.
Contact Us
How can we help?